Wind Energy – Floating Wind
One of the largest floating offshore wind projects in the world has taken a step closer to becoming a reality with the submission of the consent application to the Scottish Government.
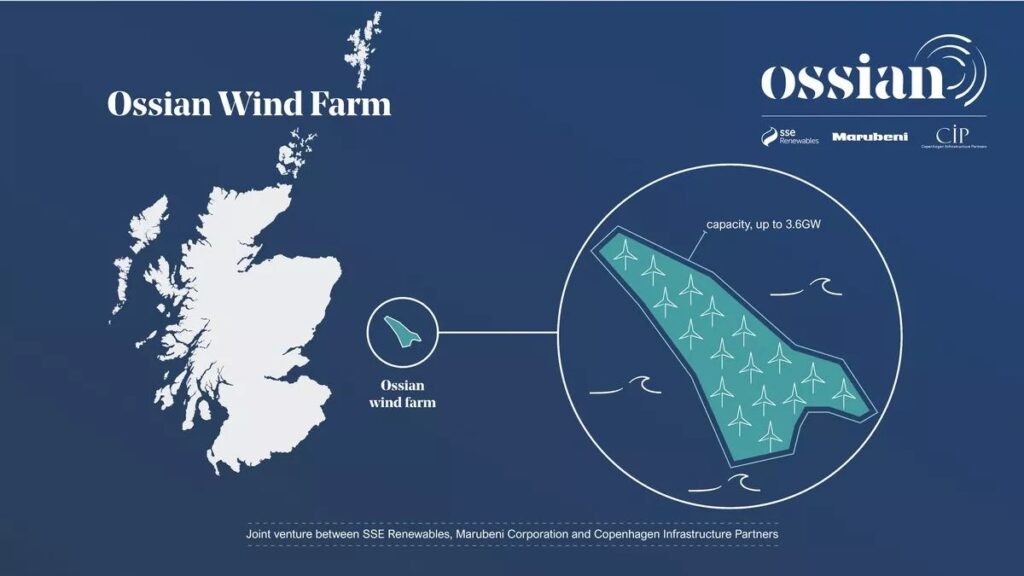
The proposed Ossian project is being co-developed off the east coast of Scotland by a partnership comprising SSE Renewables, Japanese conglomerate Marubeni Corporation, and Danish fund manager Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP).
At up to 3.6GW of installed capacity, Ossian would be among the largest floating offshore wind farms globally. Once operational, it would be capable of generating enough renewable energy to power up to six million homes annually.
Consultation and investigation work has taken place over the past three years to assess the project’s 858 km2 site, which sits 84km off the Aberdeenshire coast.
Ossian’s development lead Rich Morris said: “We have submitted a comprehensive Environmental Impact Assessment report to the Scottish Government’s Marine Directorate, and we’re committed to continuing engagement with the statutory consultees and wider stakeholder community.
“We are confident this submission will support the timely delivery of the UK’s largest floating offshore wind farm ensuring Ossian is ready to take full advantage of ongoing grid reforms and National Grid ESO’s move to a ‘first ready, first connected’ model.”
Ossian has consulted with more than 30 organisations, including regulatory and industry bodies across nature conservation, fisheries, aviation, shipping and navigation, to ensure the application is reflective of their views.
Extensive surveys have also gathered enormous amounts of key data relating to the wind farm array. This includes Ossian’s collaboration with other ScotWind developers to document the habits of bird populations in the wider North Sea region.
In November 2023, Ossian also became the first ScotWind floating offshore wind farm to complete geotechnical surveys. Earlier this year, a year-long metocean data gathering campaign collecting information relating to wave height, currents, tides and sediment movements was concluded.
